What role do you see solar-plus storage solutions playing in accelerating India’s transition towards a sustainable and reliable energy future, particularly in addressing grid stability challenges?
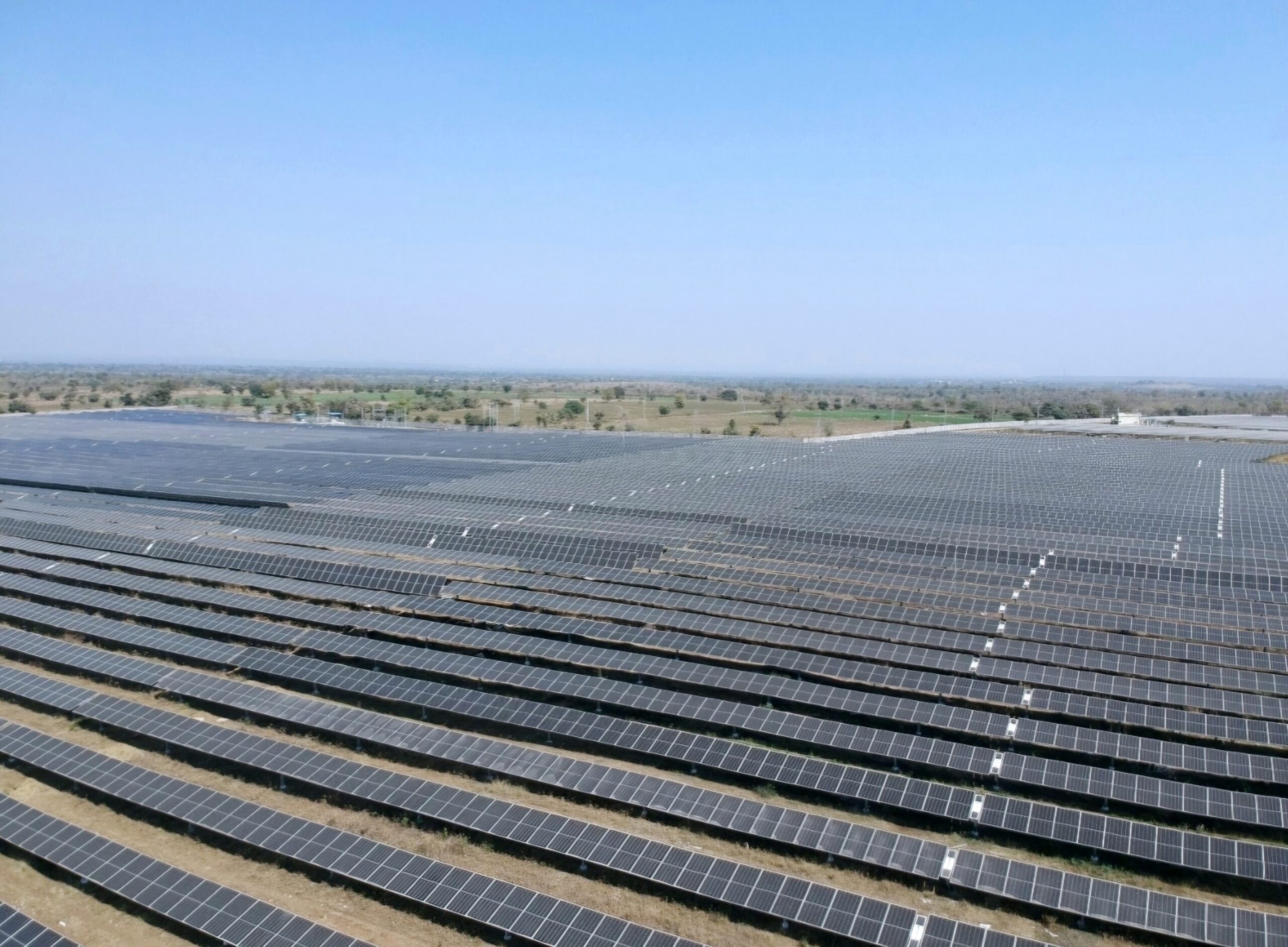
India plans to achieve net zero by 2070. We also have a 500 GW target of non-fossil capacity by 2030. As per the National Electricity Plan (NEP) by the Central Electricity Authority (CEA), India plans to install 364 GW of solar by FY 2031–32. With such high penetration of solar, its intermittent and variable nature poses grid stability challenges. By integrating storage, particularly battery storage, we can overcome these challenges. With solar coming out as the cheapest source of energy, integration with battery storage makes it a strong enabler for accelerating India’s transition towards a sustainable, resilient, and reliable energy future.
How can policy frameworks in India be enhanced to support the integration of large-scale energy storage with solar projects, and what specific policy gaps do you think need urgent attention?
The recent advisory from the Ministry of Power (MoP) comes as a welcome surprise, mandating that all new solar plants include a minimum of 2 hours of storage, with a capacity equivalent to 10% of their installed solar photovoltaic (PV) capacity. Additionally, the introduction of the Firm and Dispatchable Renewable Energy (FDRE) and Round-the-Clock (RTC) tenders, which facilitate storage integration, is a positive step forward.
However, certain policy gaps remain. Many tenders lack confirmed off-takers, preventing them from materialising into Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) with distribution companies. Another key policy gap is the need to enable storage assets to participate in multiple revenue streams, ensuring their economic viability sustainability.
What are the most cost-effective energy storage technologies suitable for the Indian solar market, and how do they compare in terms of scalability and efficiency?
In the Indian solar market, battery storage systems are emerging as the most cost-effective storage solution, driven by the rapid decline in battery prices observed in recent market discoveries. Co-locating solar with battery storage can further reduce costs by lowering integration expenses, making it a scalable and efficient solution for India’s energy transition. This trend was evident in a SECI’s recent auction, where the tariff for co located solar (2GW PV) and battery storage (1GW/4GWh) projects was in the range of INR 3.52/kWh.
How can decentralized solar-plus storage solutions be leveraged to improve energy access and resilience in rural and underserved areas of India?
Decentralised solar and storage solutions can provide a reliable power supply in areas prone to frequent grid failures while also being environmentally sustainable, as they eliminate dependence on fossil fuels. However, for these solutions to be effectively deployed in rural and underserved areas of India, a robust financial model is essential to support the transition. Ensuring economic viability at the decentralised level is crucial for widespread adoption and long-term sustainability.
Additionally, with the PM-KUSUM and PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana driving the rapid adoption of decentralised solar, integrating distributed storage alongside these initiatives would further scale deployment and contribute to cost reductions in both the solar and storage sectors.
What role do you think public-private partnerships and innovative financing models can play in scaling up solar with storage deployments across India?
To scale up solar-plus-storage deployments across India, innovative financing models are essential to mitigate project risks and drive widespread adoption of the technology. While viability gap funding (VGF) is currently available for battery projects, it should be extended to integrated solar and storage projects to enhance financial viability.
What role do you think public-private partnerships and innovative financing models can play in scaling up solar with storage deployments across India?
CSTEP has recently initiated a project to assess the energy storage requirements for co-located renewable energy projects, quantify and compare the costs and benefits of integrating storage with renewables, and evaluate the technical and economic performance of coupled storage solutions. The study aims to identify the value propositions of renewable-storage integration and its potential impact on enhancing grid stability and efficiency.